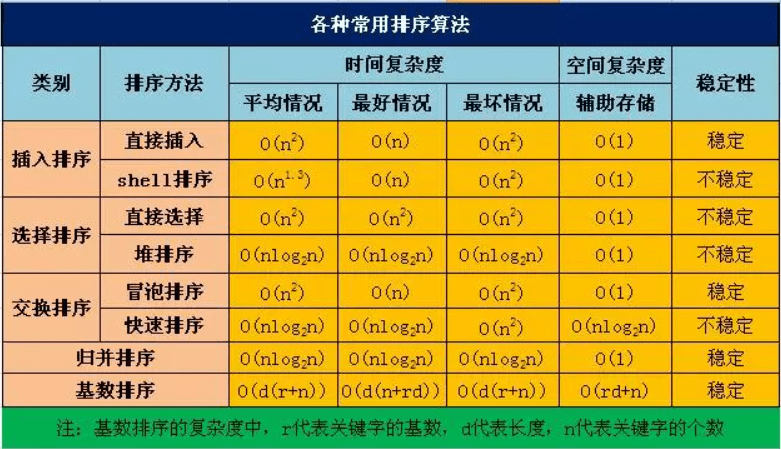
# 排序
# 冒泡排序
/**
* 冒泡排序算法
*
* @author MinChiang
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2020-03-20 9:20
*/
public class BubbleSort<T extends Comparable<T>> extends AbstractSortable<T> {
/**
* 冒泡排序
* 两两交换元素,把较大的元素置换到后面,一轮结束后最大的元素放置到最后一位
* 比较轮次:arr.length - 1,因为到最后一轮只有一个元素,无需排序
* 两两交换次数:length - 1 - 当前轮次
*
* @param arr 排序的数组
*/
public void sort(int[] arr) {
int tmp;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
tmp = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
arr[j] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# 插入排序
/**
* 插入排序算法
*
* @author MinChiang
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2020-03-20 9:41
*/
public class InsertSort<T extends Comparable<T>> extends AbstractSortable<T> {
/**
* 插入排序
* 从位置为1开始,如果当前的位置数字小于前面一个的数字,那么就进行交换处理
* 开始位置:位置为1,因为第一个元素不需要进行和前面的元素比较
*
* @param arr 待排序的数组
*/
public void insertSort(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = i; j > 0; j--) {
if (arr[j] < arr[j - 1]) {
int tmp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j - 1];
arr[j - 1] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# 选择排序
/**
* 选择排序算法
*
* @author MinChiang
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2020-03-20 8:57
*/
public class SelectSort<T extends Comparable<T>> extends AbstractSortable<T> {
/**
* 选择排序(最好写的算法了)
* 循环遍历数组,开始时候以当前遍历的首个元素为基准
* 每一轮选择都选择本轮的最小的元素,当一轮结束后,把最小的元素和当前开始的元素进行交换
* 循环次数:次数为length - 1,最后的一个元素是不用进行遍历处理的
*
* @param arr 待排序的数组
*/
public void sort(int[] arr) {
// 需要找出最小元素的所需轮次
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
int min = i;
// 因为需要和当前的第一个元素进行交换处理,因此要从i + 1开始
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[min]) {
min = j;
}
}
int tmp = arr[min];
arr[min] = arr[i];
arr[i] = tmp;
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
# 归并排序
/**
* 归并排序算法
*
* @author MinChiang
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2020-03-20 11:24
*/
public class MergeSort<T extends Comparable<T>> extends AbstractSortable<T> {
/**
* 归并排序
* 排序思想:分治法(递归)
* 停止条件:排序区域元素个数小于等于1,即begin >= end的情况
* 包含几个操作:
* 1. 分割:把当前的数组分割成为两个部分,直到不可分(begin >= end的情况)
* 2. 排序:两个数组分别定义left和right指针,分别指向左右两个数组,新建一个大小为end - begin + 1,把两个数组从小到大放入数组中
* 3. 合并:把临时数组中的内容拷贝回去原始数组中
*
* @param arr 待排序的数组
*/
public void sort(int[] arr) {
recursion(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
}
/**
* 递归处理
*
* @param arr 待排序的数组
* @param begin 开始下标(包含)
* @param end 结束下标(包含)
*/
private void recursion(int arr[], int begin, int end) {
if (begin >= end) {
return;
}
// half是表示这个位置前的下标元素都
int half = (end + begin) / 2;
// 拆分处理
recursion(arr, begin, half);
recursion(arr, half + 1, end);
// 新建数组进行临时存储,把左右两边的内容进行拷贝到临时数组中
int left = begin, right = half + 1, current = 0;
int[] tmp = new int[end - begin + 1];
while (left <= half && right <= end) {
if (arr[left] < arr[right]) {
tmp[current++] = arr[left++];
} else {
tmp[current++] = arr[right++];
}
}
while (left <= half) {
tmp[current++] = arr[left++];
}
while (right <= end) {
tmp[current++] = arr[right++];
}
// 把临时数组中的内容拷贝回原来的数组中
for (int i = 0; i < tmp.length; i++) {
arr[begin + i] = tmp[i];
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
# 快速排序
/**
* 快速排序算法
*
* @author MinChiang
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2020-03-20 8:57
*/
public class QuickSort<T extends Comparable<T>> extends AbstractSortable<T> {
/**
* 快速排序(最复杂的算法,但是效率最高)
* 本质上就是每轮选取一个基准,把所有小于此基准的元素放在基准左边,把大于此基准的元素放到右边
* 排序思想:分治法(递归)
* 基准选取:每轮的首元素
* 停止条件:排序区域元素个数小于等于1,即begin >= end的情况
* 排序原则:
* 1. 设置mark标记位,起始位置为pivot的位置,比pivot小的在左,比pivot大的在右
* 2. 当扫描到的元素比pivot小时,先移动mask(mask++),再交换mask所指元素和当前元素
* 3. 当轮排序完成后把mask所指元素和pivot交换
*
* @param arr 排序的数组
*/
public void sort(int[] arr) {
recursion(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
}
/**
* 递归处理
*
* @param arr 排序的数组
* @param begin 开始下标位置(包含)
* @param end 结束下标位置(包含)
*/
private void recursion(int[] arr, int begin, int end) {
//递归结束条件
if (begin >= end) {
return;
}
// 设置一个比较的中间基准,小于此基准的都在左边,大于此基准的都在右边
int pivot = arr[begin], mark = begin;
for (int i = begin + 1; i <= end; i++) {
// 若遍历到的元素小于基准,则说明mark要右移一位
if (arr[i] < pivot) {
mark++;
int tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[mark];
arr[mark] = tmp;
}
}
// 最后需要交换mark和基准的位置
int tmp = arr[mark];
arr[mark] = pivot;
arr[begin] = tmp;
// 递归处理
recursion(arr, begin, mark - 1);
recursion(arr, mark + 1, end);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
# DFS
特点:
- 其实就是回溯算法
- 穷举,暴力算法
- 空间复杂度比较小
伪代码如下:
result = []
def backtrack(已经选择的路径, 剩余选择列表):
if 满足结束条件:
// 此时注意路径的可变动方式,若为数组或者列表需要new一个新的
result.add(已经选择的路径)
return
for 选择 in 剩余选择列表:
// 做选择(其实就是路径的变动,把剩余选择列表中变为路径)
backtrack(路径, 选择列表)
撤销选择(回滚路径的变动)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
/**
* @author MinChiang
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2021-02-20 15:40
*/
public class Permutations {
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> choice = new ArrayList<>();
for (int num : nums) {
choice.add(num);
}
permute(new ArrayList<>(), choice, result);
return result;
}
// path表示【已经选择的路径】,choice表示【还未选择的路径】
public void permute(List<Integer> path, List<Integer> choice, List<List<Integer>> result) {
// 结束判定
if (choice.size() == 0) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < choice.size(); i++) {
// 做出选择,把未选择的路径转化为已选择的路径
int c = choice.remove(i);
path.add(c);
// 递归
permute(path, choice, result);
// 撤销选择
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
choice.add(i, c);
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
# 限流
# 计数器法
思路简单,使用方便,会有临界问题,即所有流量在临界点前后流入,会导致tps激增为2倍的tps。
public class Counter {
//初始时间
private long startTime;
//流量计数
private long count;
//滑窗大小
private long length;
//单个滑窗内最大的并发数
private long limit;
public Counter(long length, long limit) {
this.length = length;
this.limit = limit;
reset();
}
private void reset() {
this.count = 0;
this.startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public boolean require() {
if (System.currentTimeMillis() <= startTime + length) {
return ++count < limit;
}
reset();
return ++count < limit;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
# 滑动窗口
滑动窗口使用一个固定大小的数组或者链表存放细分后的数据,数组内存放单位时间内的流量计数,流量进入时,若当前的时间戳大于最后一个数组元素的时间戳,则新建元素并推移时间窗口;然后统计流量总数,若大于流量总数,则直接返回超过流量;若小于流量总数,则流量总数加一并且返回成功。本质上来说,滑动窗口的数量越多,颗粒度越高,计算的资源也越多,也会越精确。
public class RollingWindow {
private static final int DEFAULT_WINDOW_SIZE = 10;
//窗口大小,窗口越小流量越平滑
private int windowSize = DEFAULT_WINDOW_SIZE;
private final long maxTransaction;
private final long milliseconds;
private Window head;
private Window tail;
private int currentWindowLength;
private long currentCount;
private long startTime;
public RollingWindow(long milliseconds, long maxTransaction, int windowSize) {
this.windowSize = windowSize;
this.milliseconds = milliseconds / windowSize;
this.maxTransaction = maxTransaction;
Window current = new Window(0);
head = current;
tail = current;
currentWindowLength++;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
private void appendWindow() {
Window current = new Window(0);
if (currentWindowLength < windowSize) {
currentWindowLength++;
} else {
currentCount -= head.count;
head = head.next;
}
tail.next = current;
tail = current;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public boolean require() {
if (System.currentTimeMillis() <= startTime + milliseconds) {
if (currentCount >= maxTransaction) {
return false;
}
tail.count++;
currentCount++;
return true;
}
appendWindow();
if (currentCount >= maxTransaction) {
return false;
}
tail.count++;
currentCount++;
return true;
}
private static class Window {
long count;
Window next;
public Window(long count) {
this.count = count;
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
# 漏桶算法
public class LeakyBucket {
private static final int DEFAULT_WINDOW_SIZE = 10;
private int windowSize = DEFAULT_WINDOW_SIZE;
private final long maxTransaction;
private final long milliseconds;
private final long singlePeriodTransaction;
//时间执行器
private final ScheduledExecutorService executor;
//桶
private final Queue<Water> queue;
public LeakyBucket(long milliseconds, long maxTransaction, int windowSize) {
this.windowSize = windowSize;
this.milliseconds = milliseconds / windowSize;
this.maxTransaction = maxTransaction;
this.singlePeriodTransaction = maxTransaction / windowSize;
//设置桶和桶大小
queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(new Long(maxTransaction).intValue());
//单线程的任务执行器
this.executor = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
//启动任务,循环漏水
executor.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
int count = 0;
while (count++ < singlePeriodTransaction) {
Water water = queue.poll();
if (water == null) {
return;
}
water.start();
}
}, 0, this.milliseconds, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
/**
* 注水
* @param water 注入的水
*/
public void fillWater(Water water) {
this.queue.add(water);
}
public static interface Water {
void start();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
# 令牌桶算法
1
# 随机算法
# 蓄水池采样算法
1
# 洗牌算法
简单摘自Collections.shuffle
思路:
- 第0张牌随机交换下标为[0, 52)的牌
- 第1张牌随机交换下标为[1, 52)的牌
- 第2张牌随机交换下标为[2, 52)的牌
- ...
- 第50张牌随机交换下标为[51, 52)的牌
以下是Java里面的java.util.Collections#shuffle(java.util.List<?>, java.util.Random)方法实现
public static void shuffle(List<?> list, Random rnd) {
int size = list.size();
if (size < SHUFFLE_THRESHOLD || list instanceof RandomAccess) {
for (int i=size; i>1; i--)
swap(list, i-1, rnd.nextInt(i));
} else {
Object arr[] = list.toArray();
// Shuffle array
for (int i=size; i>1; i--)
swap(arr, i-1, rnd.nextInt(i));
// Dump array back into list
// instead of using a raw type here, it's possible to capture
// the wildcard but it will require a call to a supplementary
// private method
ListIterator it = list.listIterator();
for (int i=0; i<arr.length; i++) {
it.next();
it.set(arr[i]);
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# Leetcode
# 必会
- 快速排序、归并排序、堆排序
- 二叉树前中后、层序、Z字遍历,迭代+递归
- 反转链表,各种反,直接反,反一段,K个一组反,
- 接雨水,单调栈
- 股票买卖,机器人寻路,动态规划
- 回溯算法,树
- 字符串
- LRU+LFU
# Hard15题目
- 25:力扣 (opens new window)
- 23:力扣 (opens new window)
- 42:力扣 (opens new window)
- 124:力扣 (opens new window)
- 72:力扣 (opens new window)
- 4:力扣 (opens new window)
- 76:力扣 (opens new window)
- 239:力扣 (opens new window)
- 41:力扣 (opens new window)
- 32:力扣 (opens new window)
- 297:力扣 (opens new window)
- 460:力扣 (opens new window)
- 剑指51:力扣 (opens new window)
- 224:力扣 (opens new window)
- 135:力扣 (opens new window)
# 中等67
思路:map+双向链表,由于get和put都是必须为O(1)复杂度,因此只能用map
- 215:力扣 (opens new window)
- 15:力扣 (opens new window)
- 102:力扣 (opens new window)
- 103:力扣 (opens new window)
- 236:力扣 (opens new window)
- 33:力扣 (opens new window)
- 5:力扣 (opens new window)
- 200:力扣 (opens new window)
- 46:力扣 (opens new window)
- 92:力扣 (opens new window)
- 142:力扣 (opens new window)
- 54:力扣 (opens new window)
- 300:力扣 (opens new window)
- 143:力扣 (opens new window)
- 199:力扣 (opens new window)
- 56:力扣 (opens new window)
- 19:力扣 (opens new window)
- 82:力扣 (opens new window)
- 8:力扣 (opens new window)
- 148:力扣 (opens new window)
- 2:力扣 (opens new window)
- 151:力扣 (opens new window)
- 93:力扣 (opens new window)
- 105:力扣 (opens new window)
- 31:力扣 (opens new window)
- 1143:力扣 (opens new window)
- 22:力扣 (opens new window)
- 129:力扣 (opens new window)
- 113:力扣 (opens new window)
- 98:力扣 (opens new window)
- 43:力扣 (opens new window)
- 78:力扣 (opens new window)
- 470:力扣 (opens new window)
- 322:力扣 (opens new window)
- 64:力扣 (opens new window)
- 718:力扣 (opens new window)
- 48:力扣 (opens new window)
- 165:力扣 (opens new window)
- 39:力扣 (opens new window)
- 34:力扣 (opens new window)
- 153:力扣 (opens new window)
- 62:力扣 (opens new window)
- 128:力扣 (opens new window)
- 221:力扣 (opens new window)
- 240:力扣 (opens new window)
- 24:力扣 (opens new window)
- 695:力扣 (opens new window)
- 198:力扣 (opens new window)
- 498:力扣 (opens new window)
- 662:力扣 (opens new window)
- 79:力扣 (opens new window)
- 145:力扣 (opens new window)
- 402:力扣 (opens new window)
- 59:力扣 (opens new window)
- 230:力扣 (opens new window)
- 328:力扣 (opens new window)
- 61:力扣 (opens new window)
- 50:力扣 (opens new window)
- 47:力扣 (opens new window)
- 450:力扣 (opens new window)
- 74:力扣 (opens new window)
- 189:力扣 (opens new window)
- 40:力扣 (opens new window)
- 11:力扣 (opens new window)
- 114:力扣 (opens new window)
